Last week Community Health Maps traveled to Boulder, Colorado to teach a pre-conference workshop at Rising Voices 7. The theme was Converging Voices: Building relationships and practices for intercultural science. The conference was hosted by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). The workshop was well attended with about two dozen participants representing numerous AI/AN tribes and other organizations. These workshop was part of the Community Health Maps project and was funded by the National Library of Medicine (funding for the workshop was provided under a sub-award from the National Library of Medicine to ICF International).The goal of Rising Voices is to "advance science through collaborations". Participants learn how indigenous and western scientific knowledge systems can compliment one another and advance our understanding of important issues in our communities. The focus is on climate. At three hours the workshop was slightly shorter than normal. This allowed us to focus on field data collection with Fulcrum and web mapping with Carto. With a few minutes to spare Kurt Menke shared QGIS. Since he didn't have time to really demonstrate the use of QGIS he focused on the open source aspect. As an open source project, QGIS is both GIS software and a community. As such it aligns with the ethics many communities try to foster at Rising Voices.
At three hours the workshop was slightly shorter than normal. This allowed us to focus on field data collection with Fulcrum and web mapping with Carto. With a few minutes to spare Kurt Menke shared QGIS. Since he didn't have time to really demonstrate the use of QGIS he focused on the open source aspect. As an open source project, QGIS is both GIS software and a community. As such it aligns with the ethics many communities try to foster at Rising Voices.
Community Health Mapping: A New Year Review
To start the New Year I thought I’d begin with a review of Community Health Mapping (CHM). There are a lot of new project partners, and I thought it would be a good time to give a project overview. CHM is a collaborative effort between the National Library of Medicine, Center for Public Service Communications and Bird’s Eye View. The National Library of Medicine is funding the initiative.The overall goal is to empower community organizations serving vulnerable or underserved populations with low cost, intuitive mapping technology. Therefore we’ve been working with programs organizations who:
- Focus on vulnerable populations
- Frequently use and collect data
- Need effective, scalable & easy to use mapping tools
- Lack resources (i.e., for proprietary GIS training & software)
We have identified a suite of tools that allow you to collect custom field data, analyze that data, combine it with other spatial datasets, and generate both static maps and/or dynamic maps on the internet. This allows organizations to collect and work with their own data, and if appropriate, share it with others. CHM involves three components that meet all basic mapping needs:
- Field Data Collection
- Desktop Analysis and Cartography
- Internet Mapping
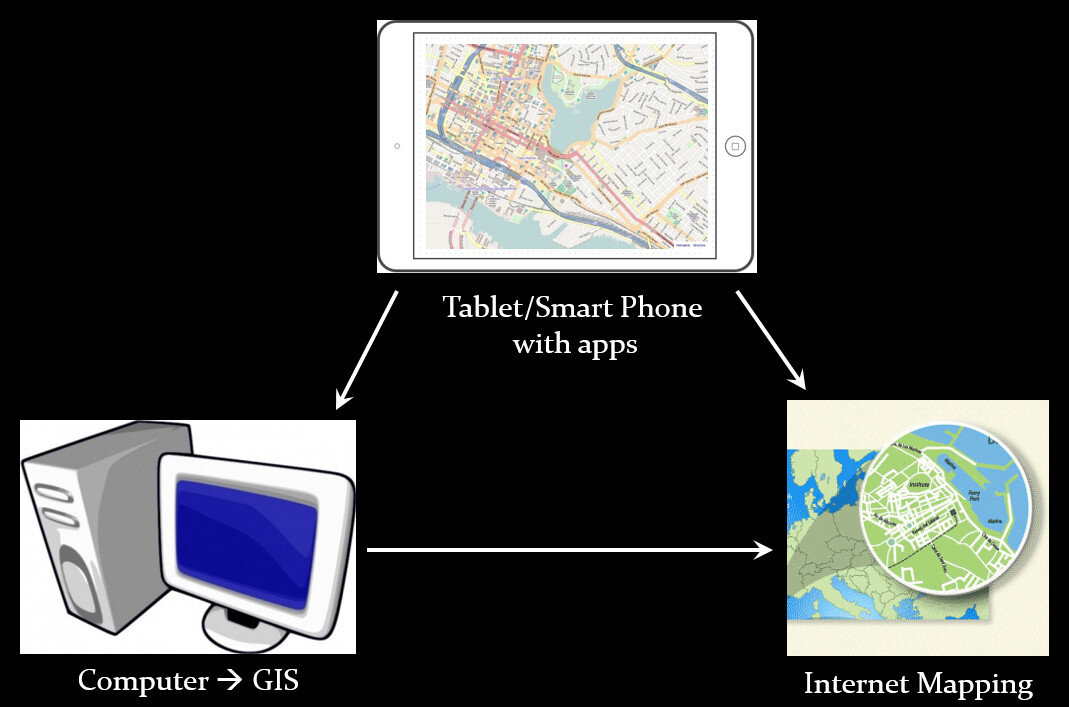 A given project may not require all three, however, collectively these components address the basic needs of all mapping projects.Field Data Collection:Rather than focusing on the use of expensive GPS receivers, we recommend the use of smart phones and tablets for these reasons:
A given project may not require all three, however, collectively these components address the basic needs of all mapping projects.Field Data Collection:Rather than focusing on the use of expensive GPS receivers, we recommend the use of smart phones and tablets for these reasons:
- Most community-based organizations already have them!
- Many know how to use them
- They're intuitive
- They're portable
- They come with an on board GPS receiver (iPhone 5 uses GPS + GLONASS)
- Have on board cameras
- Can connect to wireless networks
- Access to the internet
- Email is available
- “There's an app for that!”
 Of course an important consideration is horizontal accuracy. You can read our blog post on that topic to see if mobile smart devices meet your project needs.When collecting data you need to be able to develop your own custom data collection form. The top three mobile apps we have found are:
Of course an important consideration is horizontal accuracy. You can read our blog post on that topic to see if mobile smart devices meet your project needs.When collecting data you need to be able to develop your own custom data collection form. The top three mobile apps we have found are:
- Fulcrum: Easiest to use - iOS & Android – low monthly subscription - http://www.fulcrumapp.com/
- iForm: Slightly steeper learning curve – iOS and Android – free account - https://www.iformbuilder.com/
- ODK Collect: Easy to use – Android only – free account - https://opendatakit.org/use/collect/
Desktop Analysis and Cartography:After community field data collection, the next step typically involves bringing the data into a desktop GIS. This is the middle step in the workflow. Here the data can be viewed against basemaps such as Google or OpenStreetMap, and combined with other organizational data. This is also where analyses (proximity, density etc.) can be conducted. Presentation quality maps can also be generated in this step.The software we found to be the best fit is QGIS. This is an open source desktop GIS software. It has many strengths:
- It can consume many kinds of data, including all the data that would come out of the field data collection apps.
- It is both intuitive and robust.
- It has a large suite of geoprocessing tools for analyzing data.
- It will run on Windows, Mac, or Linux.
- It is free to download and install.
- It is well documented.
- There is a large user community.
- New functionality is being continuously added. New stable versions are being released every 4 months!
 Web PresentationOften you may want to present an interactive map of your results. Interactive means the map reader can zoom in/out, pan the map and turn layers off and on. For this we recommend CartoDB.You can sign up for a free account, which gives you 50Mb of storage space. Data can be collected with a smart phone or tablet and brought directly into CartoDB. It is a very intuitive platform. You can literally drag and drop a spreadsheet onto the CartoDB page and have the data upload to your account. It will accept the most common geospatial file formats including: spreadsheets and comma delimited text files with addresses or coordinates, KML/KMZ, GPX, and shapefiles.CartoDB also has great documentation including:
Web PresentationOften you may want to present an interactive map of your results. Interactive means the map reader can zoom in/out, pan the map and turn layers off and on. For this we recommend CartoDB.You can sign up for a free account, which gives you 50Mb of storage space. Data can be collected with a smart phone or tablet and brought directly into CartoDB. It is a very intuitive platform. You can literally drag and drop a spreadsheet onto the CartoDB page and have the data upload to your account. It will accept the most common geospatial file formats including: spreadsheets and comma delimited text files with addresses or coordinates, KML/KMZ, GPX, and shapefiles.CartoDB also has great documentation including:
- CartoDB Editor Documentation
- A comprehensive series of tutorials breaking tasks up into Basic, Medium and Advanced categories
- Tips and Tricks
- FAQ’s
 In ConclusionThis blog has a lot of resources including reviews of mapping technology and case studies. You might begin by clicking on some of the links in this entry. We are also working on a 6 lab CHM curriculum that interested parties will be able to use to hone their skills. Stay tuned for that!We are always looking for new partners and continuously work to support current project partners. If you are interested, or have questions please don't hesitate to contact John Scott (jscott at cpsc.com) or Kurt Menke (kurt at birdseyeviewgis.com). Most importantly get out and do some mapping in 2016!
In ConclusionThis blog has a lot of resources including reviews of mapping technology and case studies. You might begin by clicking on some of the links in this entry. We are also working on a 6 lab CHM curriculum that interested parties will be able to use to hone their skills. Stay tuned for that!We are always looking for new partners and continuously work to support current project partners. If you are interested, or have questions please don't hesitate to contact John Scott (jscott at cpsc.com) or Kurt Menke (kurt at birdseyeviewgis.com). Most importantly get out and do some mapping in 2016!
Wildly Successful Community Health Mapping Workshops at MUSC!
Community Health Maps (CHM) conducted it's largest and most successful workshops ever at the end of September at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC). The training at MUSC was divided into three workshops and a presentation. The attendees were a mix of professors, students and researchers, most of whom had little to no experience with GIS. Despite this fact, nearly everyone was able to collect data and make a map. This is a testament to the easy to use nature of the CHM workflow.It began Monday morning with the first workshop. This was an Intermediate Session for those Community Health Mappers who had been working on projects since the April CHM workshop. We spent two hours covering more advanced topics and answering project specific questions. Following that, Kurt Menke presented a CHM project overview at a brown bag lunch session to 30 attendees. Matt Jones closed this session with a 10 minute talk detailing how he used The Community Health Maps workflow this summer to map access to care on Johns Island.The second workshop was Monday afternoon. It was a two hour session covering field data collection with iForm, and mapping that data online with CartoDB. There were 55 attendees at this session, the vast majority of whom had no GIS experience. In just two hours all 55 attendees were able to collect field data and make a map in CartoDB!
Following that, Kurt Menke presented a CHM project overview at a brown bag lunch session to 30 attendees. Matt Jones closed this session with a 10 minute talk detailing how he used The Community Health Maps workflow this summer to map access to care on Johns Island.The second workshop was Monday afternoon. It was a two hour session covering field data collection with iForm, and mapping that data online with CartoDB. There were 55 attendees at this session, the vast majority of whom had no GIS experience. In just two hours all 55 attendees were able to collect field data and make a map in CartoDB! The final workshop on Tuesday was a 5 hour session covering the use of QGIS. The workshop consisted of a custom Charleston based QGIS exercise. Each of the 35 participants worked with a set of Charleston GIS data while learning the basic layout of QGIS. They learned how to add data, style it, and compose a map. The workshop ended with a discussion of each participants goals and project specific questions.
The final workshop on Tuesday was a 5 hour session covering the use of QGIS. The workshop consisted of a custom Charleston based QGIS exercise. Each of the 35 participants worked with a set of Charleston GIS data while learning the basic layout of QGIS. They learned how to add data, style it, and compose a map. The workshop ended with a discussion of each participants goals and project specific questions. In total almost 80 people attended one or more sections of the training! Thanks go out to Dr. Deborah Williamson for hosting the workshops, Dana Burshell for organizing the entire event and assisting during the workshops, and to Sarah Reynolds who was invaluable in providing Mac and QGIS support!
In total almost 80 people attended one or more sections of the training! Thanks go out to Dr. Deborah Williamson for hosting the workshops, Dana Burshell for organizing the entire event and assisting during the workshops, and to Sarah Reynolds who was invaluable in providing Mac and QGIS support!
Tableau Public for Data Visualizations
Tableau Public is free software that can help users publish interactive data visualizations to the internet. This software is another great option for data visualization along with GIS Cloud or CartoDB. It has powerful charting and graphing tools, and also allows you to map data and display that data against several online datasets and basemaps.No plug-ins or programming skills are required, just a browser with JavaScript enabled. Tableau Public uses a simple drag and drop process that anyone can learn. You can work with either the free Tableau Desktop app, or Tableau Online the free cloud based server. Either way you can save your work to the Tableau Public Web servers, which are accessible by everyone on the Internet. One important note about this is that any data you publish is accessible to everyone on the internet.People see and understand data, reports and dashboards faster with visual analytics technology, which can help uncover key trends, relationships, patterns, and outliers that might otherwise be a challenge to find. Tableau Public can be used to pare down information to its simplest form by stripping away the less important data.The software can connect to Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Access, and multiple text file formats. It has a limit of 1,000,000 rows of data allowed in any single file. Your organization may use up to 50 megabytes of space.Tableau Public projects can be shared by emailing a link or by embedding the work in a blog, wiki, or website. Clicking on an emailed link will open a browser page with the view loaded. If embedded onto a page, anyone who visits the page will see the live interactive view. The following shows the use of Tableau Public in two health related studies.Public Health Case StudiesTo visualize the specific social problem of teen pregnancy over time, Tableau Public was used by the Wisconsin Council on Children and Families to show the decline in births to teen mothers in Wisconsin over recent years. The data depicts racial disparities in teen births in Wisconsin as well as differences in birth rates between older and younger teens. The online link to the data visualizations created with Tableau Public for this study can be found here: http://tblsft.com/public/gallery/teen-pregnancy-declinesThe figure below is a screenshot of one of the data visualizations from this study. Data visualizations are interactive. Here the white popup window is showing data from a specific place on the line graph. Such visualizations may help communities address and manage such issues as health problems associated with prematurity and poor academic performance of children of teen parents.Data can also be mapped by geographic coordinates, city, state, county, and zip code. The visualization below deals with Medicare Costs and combines a map with a chart showing trends in the data.
Such visualizations may help communities address and manage such issues as health problems associated with prematurity and poor academic performance of children of teen parents.Data can also be mapped by geographic coordinates, city, state, county, and zip code. The visualization below deals with Medicare Costs and combines a map with a chart showing trends in the data. Other data visualization examples created with Tableau Public can be found in the Gallery:http://www.tableausoftware.com/public/galleryOther Tableau Public Resources can be found here:https://public.tableau.com/s/resources
Other data visualization examples created with Tableau Public can be found in the Gallery:http://www.tableausoftware.com/public/galleryOther Tableau Public Resources can be found here:https://public.tableau.com/s/resources
Teens Map Environmental Health of Their Community (Sea Islands, South Carolina)
By Guest Blogger: Derek Toth - Communities in Schools CharlestonThe Teen Health Leadership Program (THLP) is in their eight year of existence at St. John’s High School on Johns Island. The program gathers leaders of the school together and focuses on a health topic they feel is affecting their community and assists the community in understanding this topic through the use of media dissemination. In the past, topics included Autism, Cancer, Stress, Obesity and Alcohol and Drugs and This year, the students wanted to look at their community as a whole with a topic of Environmental Health.The THLP students wanted to see what makes their Sea Island community different. The Sea Islands are composed of John’s Island, Wadmalaw Island, Seabrook Island and Kiawah Island outside of Charleston, South Carolina. Students primarily come from John’s and Wadmalaw Islands. These islands are extremely different for many reasons. The students wanted to be able to translate these differences in a new form for the Teen Health Leadership Program. The students were presented with an opportunity to use the Community Health Mapping tools discussed on this blog, and some training made available from the National Library of Medicine. With GIS, the students can pin point differences within the islands for their community to see.(This January Kurt Menke conducted a Community Health Map training at the Medical University of South Carolina College of Nursing. Two teachers with Communities in Schools Charleston attended and the next afternoon Kurt Menke went to St. John's High School and showed the students how to map their campus with their iPhones.)  The students used smart phones, along with an app named iForm, to map points of interest with GPS. They collected well water locations, ground and city water sources, as well as, places in the community to purchase food. The food resources they mapped included farmers markets, produce stands, grocery stores and local farms. The students were able to indicate these points on a map. Google maps was used to create the final map.With the final map they were able to determine that people on Wadmalaw Island have less access to food and water than those on St. John's Island. For example, Wadmalaw Island is limited in places to buy produce or groceries, and has limited access to the farms that John’s Island has. Residents of Wadmalaw Island are on well water, and obtain their produce at the local grocery store on Johns Island, as opposed to driving to one of the many local farms.
The students used smart phones, along with an app named iForm, to map points of interest with GPS. They collected well water locations, ground and city water sources, as well as, places in the community to purchase food. The food resources they mapped included farmers markets, produce stands, grocery stores and local farms. The students were able to indicate these points on a map. Google maps was used to create the final map.With the final map they were able to determine that people on Wadmalaw Island have less access to food and water than those on St. John's Island. For example, Wadmalaw Island is limited in places to buy produce or groceries, and has limited access to the farms that John’s Island has. Residents of Wadmalaw Island are on well water, and obtain their produce at the local grocery store on Johns Island, as opposed to driving to one of the many local farms.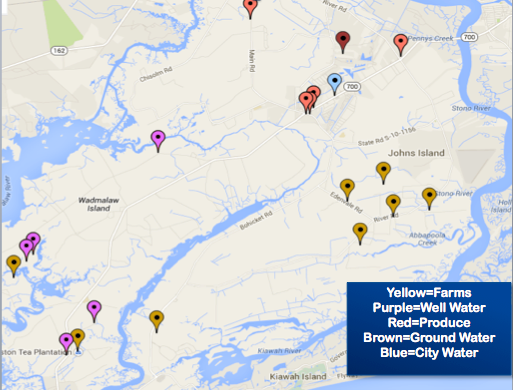 The final map was inserted into the Environmental Health project for the community to have a unique perspective of their Sea Island Community. Overall, the students felt that using their smart phones to map their community was easy to learn and fun. They were able to grasp the information quickly and seemed pleased with their results. The group feels it reached it’s goal of accomplishing a fresh look at the Sea Islands and felt it added to their presentation on Environmental Health.
The final map was inserted into the Environmental Health project for the community to have a unique perspective of their Sea Island Community. Overall, the students felt that using their smart phones to map their community was easy to learn and fun. They were able to grasp the information quickly and seemed pleased with their results. The group feels it reached it’s goal of accomplishing a fresh look at the Sea Islands and felt it added to their presentation on Environmental Health.
Using CartoDB for Beautiful Online Maps
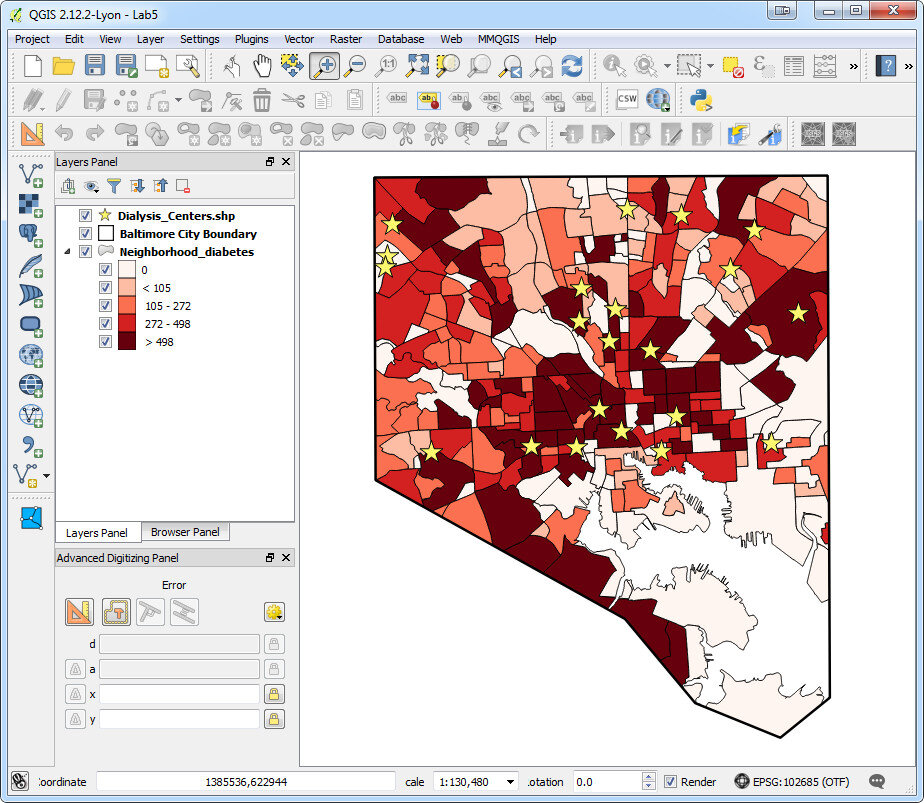
CartoDB is an online cloud based platform for storing and visualizing spatial data. It is the perfect tool for the third part of the workflow (outlined in the Introduction). You can sign up for a free account, which gives you 50Mb of storage space. Data can be collected with a smart phone or tablet with iForm, and brought directly into CartoDB. It is a very intuitive platform. You can literally drag and drop a spreadsheet onto the CartoDB page and have the data upload to your account. It will accept the most common geospatial file formats including: spreadsheets and comma delimited text files with addresses or coordinates, KML/KMZ, GPX, and shapefiles. Below is an example of a spreadsheet of Baltimore Dialysis Centers in CartoDB. This shows the spreadsheet in Data View .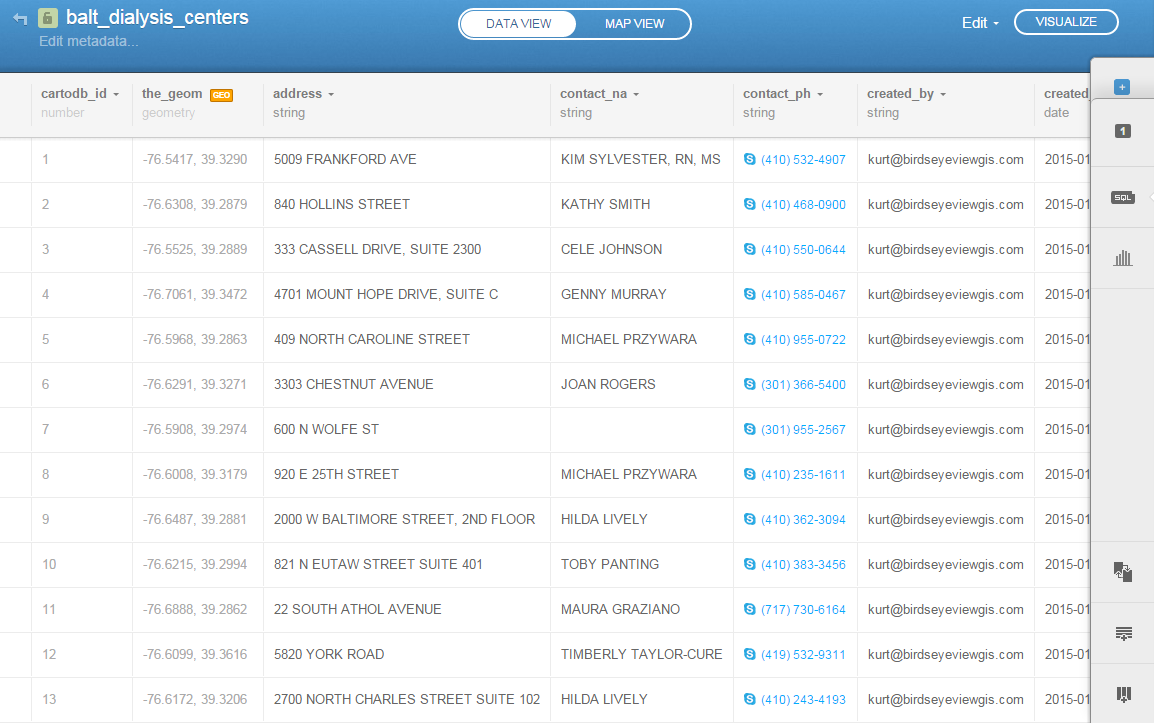 After telling CartoDB which columns contain the latitude and longitude values, the data can be viewed in Map View (below). Here the default Positron basemap is being used. There are a variety of basemaps to choose from including imagery, Stamen maps and Nokia maps.
After telling CartoDB which columns contain the latitude and longitude values, the data can be viewed in Map View (below). Here the default Positron basemap is being used. There are a variety of basemaps to choose from including imagery, Stamen maps and Nokia maps.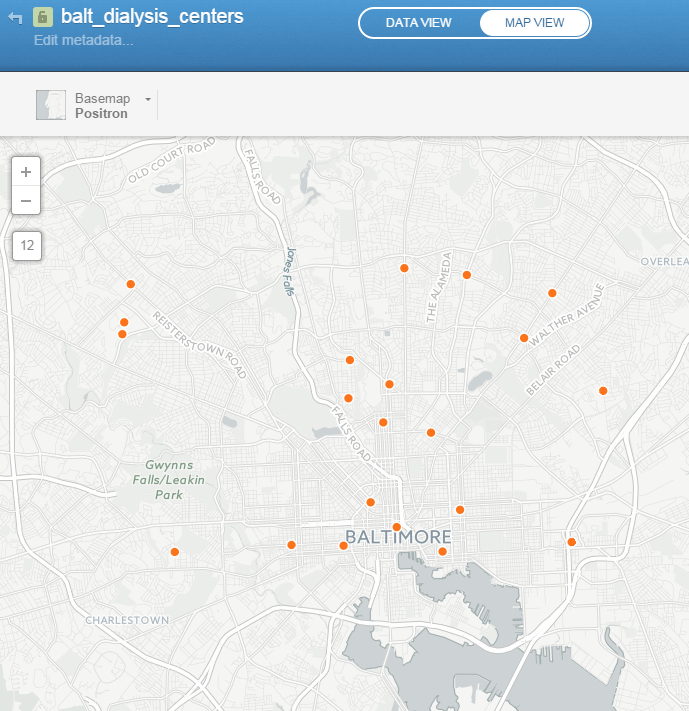 Once multiple data layers have been uploaded you can create a visualization. Below is a map focusing on Balitmore Diabetes. It includes Baltimore neighborhoods classified by the number of diabetics, food deserts and dialysis centers. CartoDB provides wizards and other tools for styling your data. The dynamic map can be accessed here: http://cdb.io/1G4xP7j
Once multiple data layers have been uploaded you can create a visualization. Below is a map focusing on Balitmore Diabetes. It includes Baltimore neighborhoods classified by the number of diabetics, food deserts and dialysis centers. CartoDB provides wizards and other tools for styling your data. The dynamic map can be accessed here: http://cdb.io/1G4xP7j Visualizations can be shared via hyperlinks and embedded into webpages. CartoDB also has great documentation including:
Visualizations can be shared via hyperlinks and embedded into webpages. CartoDB also has great documentation including:
- CartoDB Editor Documentation
- A comprehensive series of tutorials breaking tasks up into Basic, Medium and Advanced categories
- Tips and Tricks
- FAQ’s
Sign up for a free account and take it for a spin. On a related note Community Health Maps is almost done with a complete curriculum for community health mapping. It consists of six labs. The final lab shows you how to work with CartoDB from setting up an account to sharing a visualization. Stay tuned!
Community Health Maps Conducts a Training in the South Carolina Lowcountry
Recently Kurt Menke headed to Charleston, South Carolina to train several groups how to map their communities. This region is also known as the 'lowcountry' due to the flat, low elevation geography. The training was hosted by the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) and included people from Communities in Schools - Charleston (CISC) and the MUSC College of Nursing. First everyone learned how collect GPS field data with iPads. For this we used a new app named iForm. This app was used in lieu of EPI Collect, which no longer supported on iOS. (The next blog post will cover iForm in more detail.) iForm is an app very similar to the Android app ODK Collect, allowing a custom data collection form to be developed. To practice we collected bike rack locations and seating areas around the MUSC campus. The afternoon was spent working with everyone's data. GPS data points were brought into QGIS and shown against some local Charleston GIS data layers.
First everyone learned how collect GPS field data with iPads. For this we used a new app named iForm. This app was used in lieu of EPI Collect, which no longer supported on iOS. (The next blog post will cover iForm in more detail.) iForm is an app very similar to the Android app ODK Collect, allowing a custom data collection form to be developed. To practice we collected bike rack locations and seating areas around the MUSC campus. The afternoon was spent working with everyone's data. GPS data points were brought into QGIS and shown against some local Charleston GIS data layers.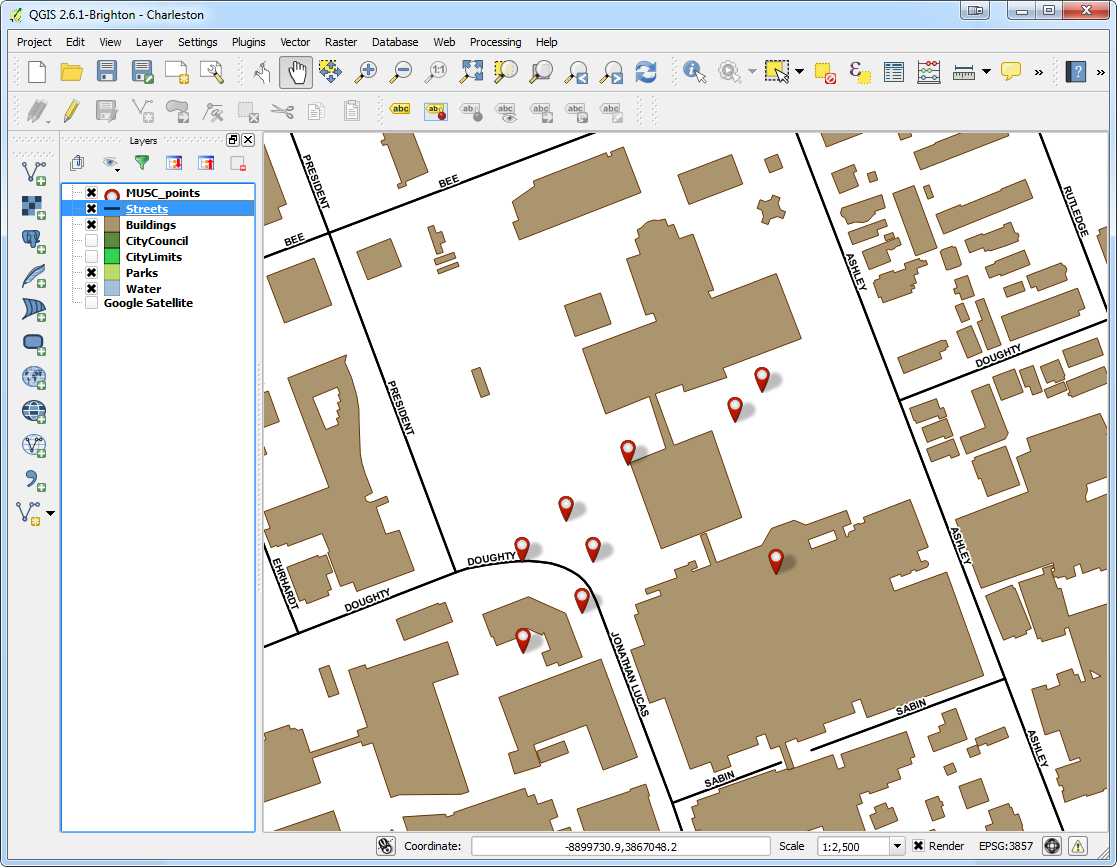 The points were also uploaded to CartoDB. CartoDB is another new component of the Community Health Mapping workflow. It has become more intuitive than GIS Cloud and worked really well. (Note: There will be a post on using CartoDB soon too.)The following day I visited CISC's Derek Toth and three of his students at St. John's High School on John's Island, SC. Over a working lunch Mr. Toth showed students how easy it is to collect GPS points with their iPhones. We collecting several points while walking around the campus.
The points were also uploaded to CartoDB. CartoDB is another new component of the Community Health Mapping workflow. It has become more intuitive than GIS Cloud and worked really well. (Note: There will be a post on using CartoDB soon too.)The following day I visited CISC's Derek Toth and three of his students at St. John's High School on John's Island, SC. Over a working lunch Mr. Toth showed students how easy it is to collect GPS points with their iPhones. We collecting several points while walking around the campus. Afterwards we went back inside and showed them how to upload the points into CartoDB and make a map. The figure below shows the results of 45 minutes worth of work! Click on the map to open the live version.
Afterwards we went back inside and showed them how to upload the points into CartoDB and make a map. The figure below shows the results of 45 minutes worth of work! Click on the map to open the live version.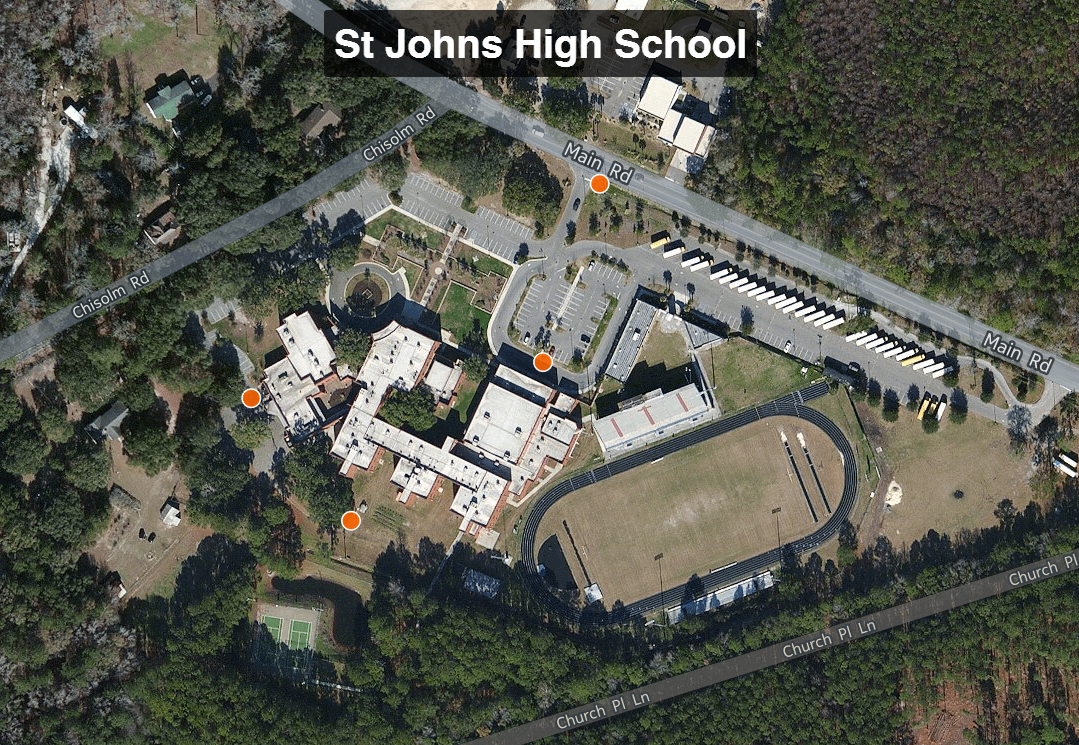 This spring these three juniors will be leading the charge to map their island! They will be presenting their work to the National Library of Medicine later this spring. I look forward to seeing their work!
This spring these three juniors will be leading the charge to map their island! They will be presenting their work to the National Library of Medicine later this spring. I look forward to seeing their work!
Technology + Youth = Change
by Chad Noble-TabioloIt all started in May 2013 when I watched the documentary entitled Revolutionary Optimists on PBS’s Independent Lens. It showed how young people from a slum in Kolkata, India were able to map the deficient and unsafe water taps in their community, in order to plea with the government for more and safe drinking water lines. The film highlighted technology in an unconventional way. It showed GIS-technology as an innovative tool to mobilize youth for social change.This heralded the beginning of a partnership with Map Your World to develop a mapping project in the Philippines in the summer of 2013. Through coordination with domestic and international partners, the youth mapping program was implemented in Southville 7 — an impoverished and neglected slum community, about three-hours south of metro Manila. The issues faced in Southville 7 ranged from lack of access to jobs, water and electricity to food insecurity and child and maternity health; and because of a lack of response from both the government and non-governmental sectors, the project was aimed to raise awareness and demand change.In just a few weeks, a dozen phones were donated. Youth, ranging from 15 to 23 years old, were trained to go house-to-house to collect data. By the end of three months, 3000 families were surveyed and the needs of the community were mapped. Depicted below is Map 1, which shows the families who have direct access to water in their homes.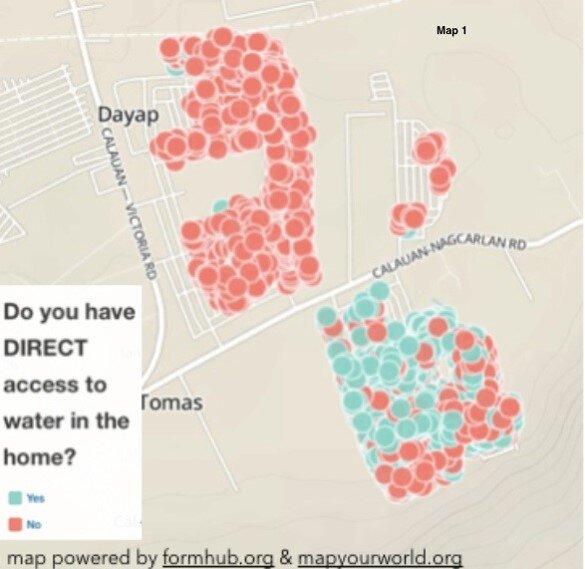 Because of the unequal distribution of resources, it was evident who had direct access to water and who did not. Map 2 shows those families who did not have direct access to water. These families had to walk more than 1 kilometer to a communal water tap.
Because of the unequal distribution of resources, it was evident who had direct access to water and who did not. Map 2 shows those families who did not have direct access to water. These families had to walk more than 1 kilometer to a communal water tap.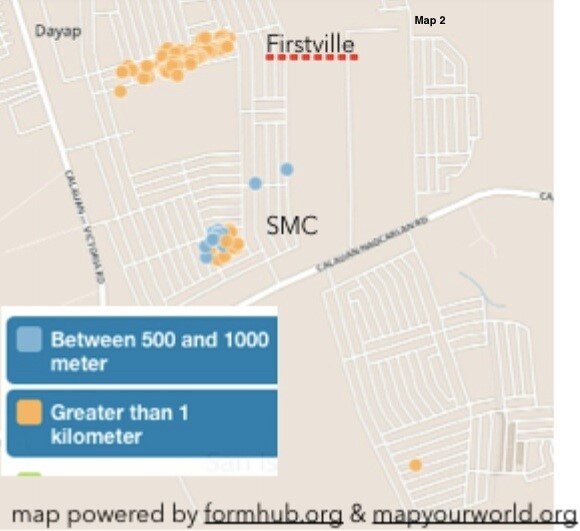 Lastly, Map 3, represents the top four needs according to the three different subdivisions or sites in Southville 7. Collectively these maps and data provide an opportunity for proper and adequate planning for public health infrastructure and needs.
Lastly, Map 3, represents the top four needs according to the three different subdivisions or sites in Southville 7. Collectively these maps and data provide an opportunity for proper and adequate planning for public health infrastructure and needs.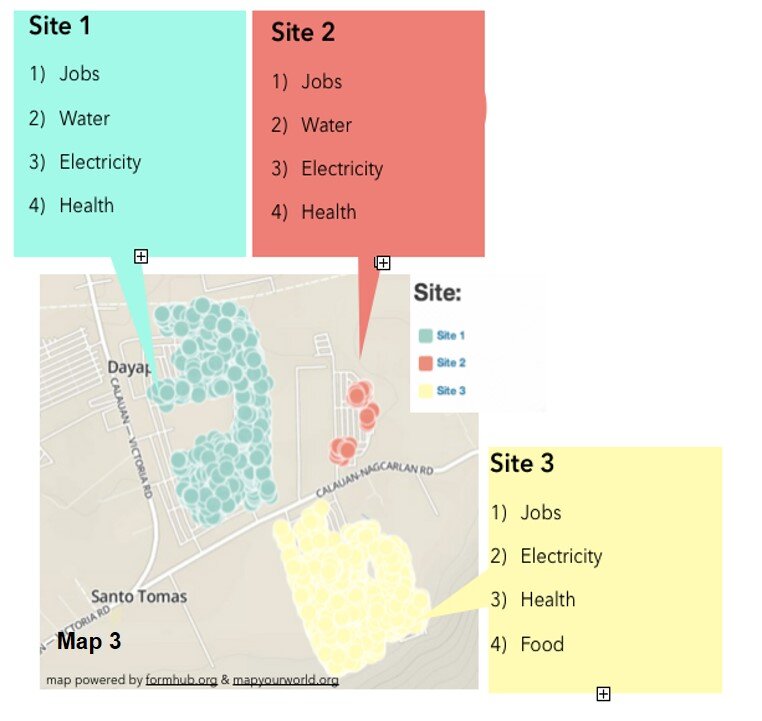 The Android mobile phones used by the youth were powered by open-source applications for GPS-mapping and data collection. ODK Collect or Open Data Kit was the data collection tool utilized in the project. It can be found on the Android market. (NOTE: This tool is also described in the Community Health Mapping blog post on Field Data Collection). This tool is functional only after uploading a survey form that is created in Microsoft Excel and uploaded to the companion site www.formhub.org. The maps were created online with Map Your World, an online community mapping tool inspired by the Revolutionary Optimists documentary.
The Android mobile phones used by the youth were powered by open-source applications for GPS-mapping and data collection. ODK Collect or Open Data Kit was the data collection tool utilized in the project. It can be found on the Android market. (NOTE: This tool is also described in the Community Health Mapping blog post on Field Data Collection). This tool is functional only after uploading a survey form that is created in Microsoft Excel and uploaded to the companion site www.formhub.org. The maps were created online with Map Your World, an online community mapping tool inspired by the Revolutionary Optimists documentary. In the end, the 30 youth involved in the mapping project were able to accomplish an endeavor that many people in their community had not expected. They were able to successfully map who in their community had access to water, electricity, jobs and vaccination for children under five years old, among others. They became leaders who are now equipped with leadership and technological skills that many in their community lack. They were empowered to raise awareness about the social injustices and health inequalities existing among them.
In the end, the 30 youth involved in the mapping project were able to accomplish an endeavor that many people in their community had not expected. They were able to successfully map who in their community had access to water, electricity, jobs and vaccination for children under five years old, among others. They became leaders who are now equipped with leadership and technological skills that many in their community lack. They were empowered to raise awareness about the social injustices and health inequalities existing among them. The Southville 7’s mapping work was primarily a vehicle for instilling hope, and the use of GPS/mapping-technology offered an opportunity for the youth to be the voice for their community. According to one youth, “For me, mapping is like knowing. Knowing the problems, and how people are coping with them. Through the work we can open the eyes of the people, not only the things that can help them, but things that can help us all.”
The Southville 7’s mapping work was primarily a vehicle for instilling hope, and the use of GPS/mapping-technology offered an opportunity for the youth to be the voice for their community. According to one youth, “For me, mapping is like knowing. Knowing the problems, and how people are coping with them. Through the work we can open the eyes of the people, not only the things that can help them, but things that can help us all.”
Display and Share Your Maps Online via GIS Cloud
The third step in the workflow (outlined in the Introduction) is to share your maps online via GIS Cloud. This is an online mapping platform. You can sign up for a free account, upload your data, and share your maps with others. The maps will be dynamic, meaning you can do things like pan and zoom, turn layers on and off and identify features. PricingYour free account comes with a Map Viewer and Map Editor and gives you 100Mb of space in your cloud account. If you require more space you can upgrade to Premium subscription which offers 1 Gb of space. Premium accounts cost $55/month.Data UploadGIS Cloud accepts all common GIS file formats and the data upload section is very intuitive. You can zip all your data and just upload the zip file and GIS Cloud will take care of the rest. You can even drag and drop files anywhere in the browser and they will upload to your account. Once uploaded it offers a nice range of options for symbolizing your data.
PricingYour free account comes with a Map Viewer and Map Editor and gives you 100Mb of space in your cloud account. If you require more space you can upgrade to Premium subscription which offers 1 Gb of space. Premium accounts cost $55/month.Data UploadGIS Cloud accepts all common GIS file formats and the data upload section is very intuitive. You can zip all your data and just upload the zip file and GIS Cloud will take care of the rest. You can even drag and drop files anywhere in the browser and they will upload to your account. Once uploaded it offers a nice range of options for symbolizing your data. Map EditorHere you have a variety of tools available including those for data editing, feature selection, basic analysis, table joins, geocoding addresses. It even has a database manager. You can create new layers in your cloud account and edit them here. With the analysis tools you can compute areas, measure proximity of one feature to another, buffer a layer by a certain distance, and create density maps.
Map EditorHere you have a variety of tools available including those for data editing, feature selection, basic analysis, table joins, geocoding addresses. It even has a database manager. You can create new layers in your cloud account and edit them here. With the analysis tools you can compute areas, measure proximity of one feature to another, buffer a layer by a certain distance, and create density maps.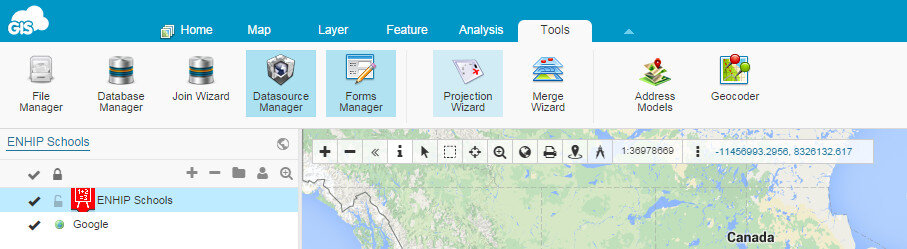 Map ViewerHere your data can be viewed against basemaps such as Google and OpenStreetMap. Your map can also be shared and published. There are several ways to share your maps. The two easiest methods are to provide the link to your map, or embed the dynamic map in a web page. Clicking the Share and Publish button opens the window below. Here you are provided the url to your map viewer and the javascript for embedding the map into a webpage. I would have embedded a dynamic map here, however, WordPress does not allow bloggers to post JavaScript on WordPress.org blogs. You can also share your map with other GIS Cloud users by Publishing the map. Click on the image below to open up the ENHIP Schools in a GIS Cloud Map Viewer window.
Map ViewerHere your data can be viewed against basemaps such as Google and OpenStreetMap. Your map can also be shared and published. There are several ways to share your maps. The two easiest methods are to provide the link to your map, or embed the dynamic map in a web page. Clicking the Share and Publish button opens the window below. Here you are provided the url to your map viewer and the javascript for embedding the map into a webpage. I would have embedded a dynamic map here, however, WordPress does not allow bloggers to post JavaScript on WordPress.org blogs. You can also share your map with other GIS Cloud users by Publishing the map. Click on the image below to open up the ENHIP Schools in a GIS Cloud Map Viewer window.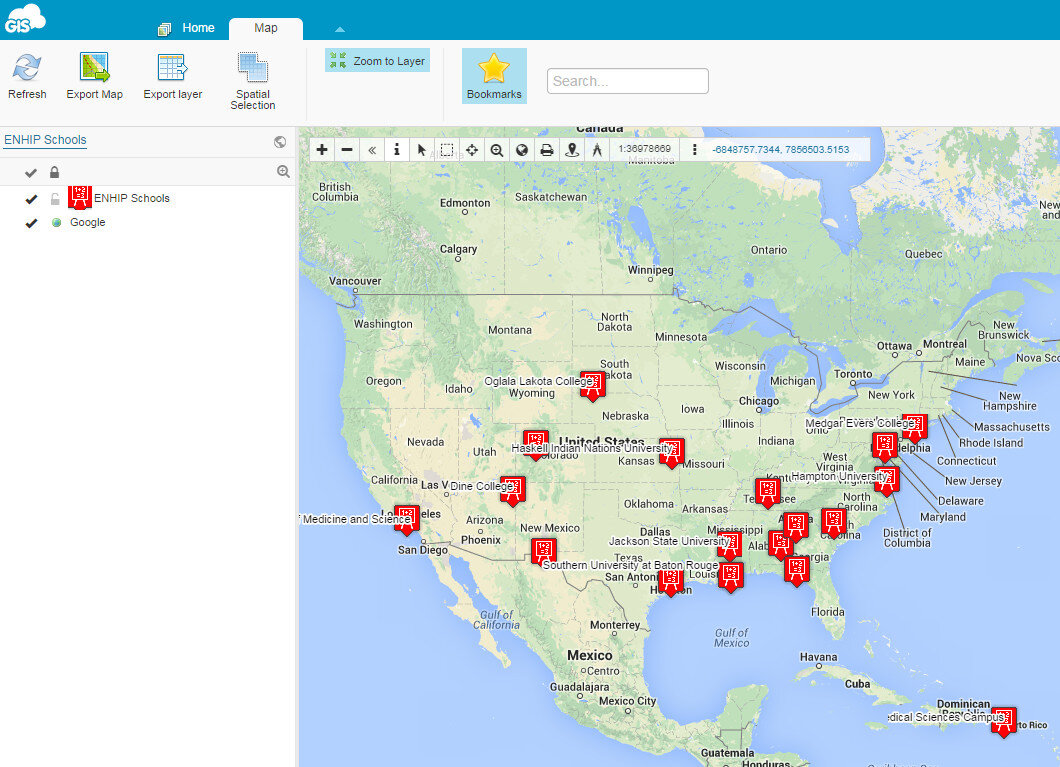 ResourcesOur Resources page has a GIS Cloud document that covers uploading data, styling data and sharing a map.There are additional online mapping platforms such as CartoDB and MangoMaps. We found GIS Cloud to be the best combination of being intuitive yet powerful. However, all three options have free licensing levels. So you can try them yourself and decide which works best for you. These other options will be covered in future posts. Happy mapping!
ResourcesOur Resources page has a GIS Cloud document that covers uploading data, styling data and sharing a map.There are additional online mapping platforms such as CartoDB and MangoMaps. We found GIS Cloud to be the best combination of being intuitive yet powerful. However, all three options have free licensing levels. So you can try them yourself and decide which works best for you. These other options will be covered in future posts. Happy mapping!
